What is an Inert Gas Glove Box?
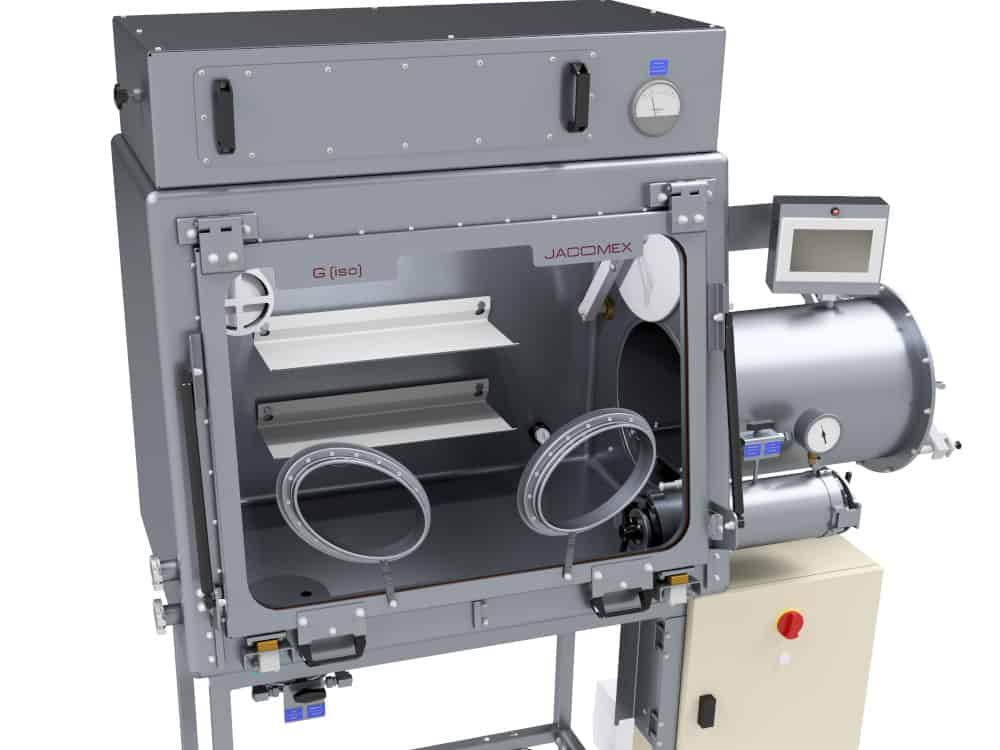
An inert gas glove box is an enclosed area used for the handling and storage of compounds and processes that are sensitive to air or moisture. Its oxygen level and hygrometry are kept below 1 ppm. The air inside the enclosure is replaced by inert or neutral gas, i.e. argon, nitrogen or helium.
The glove box for inert gas containment is equipped with various devices to assist in the circulation and purification of the inert gas. Solvents, water and oxygen are removed from the glove box and an inert environment is created. There are two types of purification systems in these gas glove boxes:
- Lost gas flushing: a permanent flow of inert gas enters and leaves the glove box to renew its atmosphere (hence the term lost gas flushing). The consumption of inert gas is significant;
- closed-loop gas purifier: the purifier purifies the atmosphere and the gas continuously thanks to a closed-loop circulation. The glove box consumes considerably less inert gas.
The internal pressure in the glove box is slightly positive, thus exceeding atmospheric pressure. The overpressure prevents ambient outside air from entering the glove box through possible micro-leaks or the gloves becoming porous over time.
Why Operate in an Inert Atmosphere?
The inert working environment within a glove box allows for safe handling of products or operations. The protective device maintains oxygen and moisture purity to prevent any reaction. It acts as a physical barrier between products/operations and the atmosphere.
To make handling possible without compromising containment, the main chamber of the glove box has transparent sides with integrated handling gloves. The number of gloves is variable depending on the needs of the workstations, the operations to be performed and the layout of the instrumentation inside. Transfer airlocks are used to transfer parts, samples and the various tools required for handling.
The inert gas glove box also has integrated safety features that guarantee its correct operation such as nitrogen, oxygen and humidity sensors, regulators, alarms and safety valves. A safety valve allows the evacuation of excess gas to prevent the glove box from becoming too pressurized. The containment conditions required for each operation are variable (temperature, pressure, protective gas, etc.) depending on the sector. It is possible to control the working environment using regulators.
An inert gas glove box can be used in many sectors. It is widely used in the aerospace industry, research and development, biology, organometallic chemistry, semiconductors, microelectronics, solid state physics, etc.
In particular, TIG welding under argon, welding and repair of titanium parts, noble alloys and super alloys such as Inconel, Hastelloy and Monels and repair of titanium parts, 3D printing, strict anaerobic experiments in biology or even to reproduce the ambient conditions of an underground environment to verify parameters such as geochemistry. Petrochemistry is also an important sector for glove boxes under inert atmospheres. Some glove boxes are even installed on off-shore platforms for use in enhanced oil recovery.