What is laser welding?
The principle of laser welding is simple: to join two metal elements permanently together by means of a laser beam that melts their two edges and without using any other joining parts. The beam in question is as thin as a hair or even thinner, but it brings the metal to its vaporization and/or melting point. The melt bath created makes it possible to assemble the parts to be welded. Thanks to the delicacy and precision of the technique, the results are simply perfect and difficult to detect with the naked eye.
In general, laser welding can be used to weld steel, stainless steel, inconel, tantalum, titanium, nickel, etc. There are, however, metals that cannot be welded in the open air because of a high risk of oxidation. These include titanium, tantalum and molybdenum. Welds made in the open air on these metals can be more fragile and brittle. An example of this can be seen with titanium, which becomes blue or grey in contact with oxygen in these cases. To avoid these problems, laser welding should be carried out in a glovebox under inert gas.
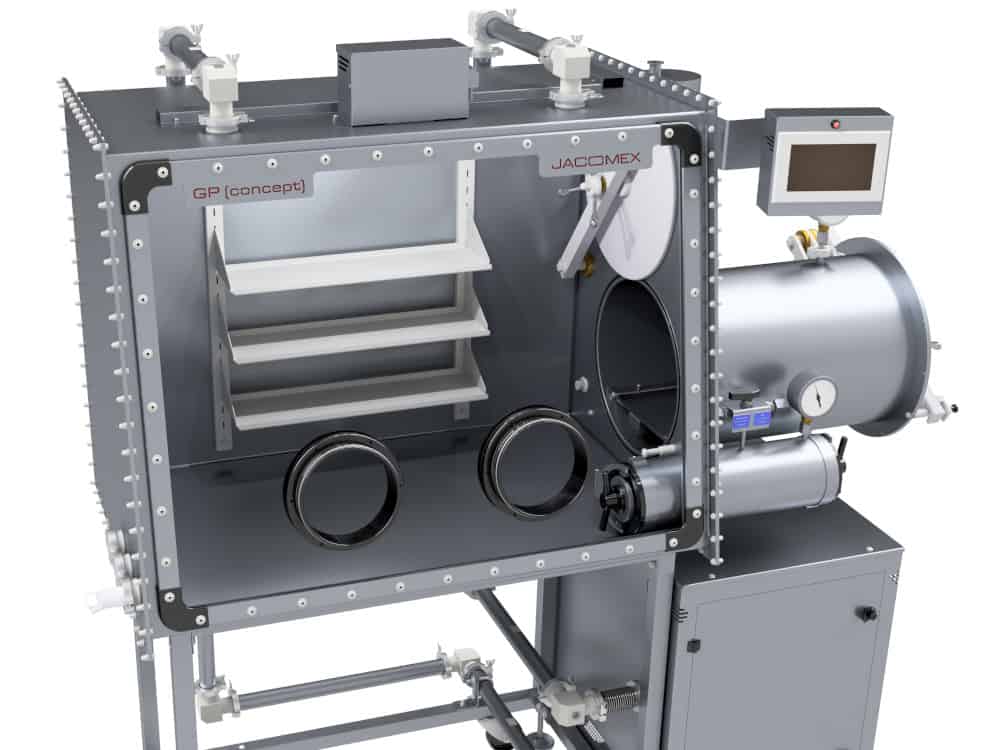
The glovebox for laser welding
In the knowledge that the ambient air is likely to alter the mechanical characteristics of the metals to be welded, laser welding in the glovebox will allow you to operate in a safe atmosphere. In this enclosure, the welding area is surrounded by a shielding gas such as argon, helium or a mixture of these two gases in order to protect it.
The role of the glovebox for welding
The gas purification unit controls the moisture and oxygen content in ppm to ensure that the strength and quality of the assembly complies with current standards. The role of the glovebox is, therefore, to confine the area away from the air and prevent the propagation of these protective gases. There is a reduction in the heat-affected zone (HAZ), less coloration on the parts to be assembled, better mechanical resistance of the weld over time and greater precision. You avoid deformations while saving time. As a bonus, it becomes easier to weld the most difficult-to-access places or extremely thin surfaces with this equipment.
Other glovebox applications
The applications of a glovebox are not limited to laser welding. It is often used for TIG and inert gas welding, both in the metallurgical, aeronautical and nuclear industry as well as in research and development, the energy sector, etc. Welding technology can differ depending on the objectives. Examples: edge-to-edge welding, welding with or without added material, spot welding, transparency welding, lap welding, etc.
For best welding performance and a perfect appearance, it is essential that laser welding takes place in a glovebox. Suppliers such as Jacomex offer ranges of gloveboxes adapted to this application. They are a global benchmark in the manufacture of containment solutions.